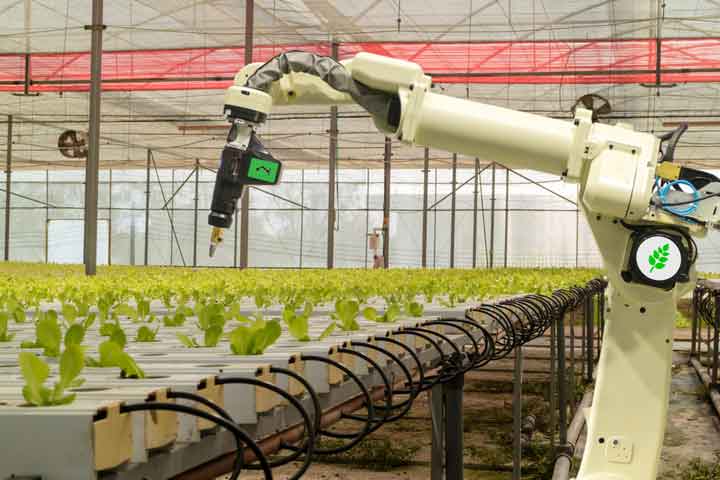
Robotic Innovations in Precision Agriculture: Transforming Crop Yields and Efficiency

Introduction to Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture integrates advanced technologies, including robotics, artificial intelligence, and IoT, to optimize farming processes. By using robotics, farmers can achieve higher efficiency, reduce resource wastage, and improve overall crop yields. Automated systems analyze soil conditions, monitor plant health, and perform labor-intensive tasks with precision, ensuring sustainable and profitable farming.
Key Applications of Robotics in Agriculture
1. Automated Planting and Seeding
- Robotic seed planters use GPS and AI-driven algorithms to place seeds at optimal depths and spacing, ensuring uniform germination and maximizing land usage.
- Drones and autonomous ground vehicles assist in aerial seeding, particularly in hard-to-reach areas.
2. Precision Irrigation and Water Management
- Smart irrigation robots use sensors to analyze soil moisture and apply water where needed, reducing water wastage.
- Automated irrigation systems integrate with weather forecasting models to adjust watering schedules based on environmental conditions.
3. AI-Powered Pest and Weed Control
- Autonomous robots equipped with cameras and AI can detect weeds and pests, allowing for targeted pesticide application rather than blanket spraying.
- Laser and mechanical weeding robots eliminate unwanted plants without herbicides, promoting eco-friendly farming.
4. Soil Health Monitoring and Nutrient Management
- Robotic systems collect real-time soil samples and analyze nutrient levels, helping farmers optimize fertilizer application.
- AI-driven analytics recommend precise nutrient distribution, preventing soil degradation and ensuring optimal crop health.
5. Automated Harvesting and Crop Sorting
- Robotic harvesters use machine vision and robotic arms to pick fruits and vegetables with minimal damage, improving efficiency and reducing labor dependency.
- Sorting robots classify crops based on size, color, and quality, ensuring only the best produce reaches the market.
6. Crop Health Surveillance with Drones and Sensors
- Aerial drones equipped with multispectral cameras monitor crop health, detecting early signs of disease, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies.
- AI-powered analytics process the drone-collected data to recommend targeted interventions, preventing large-scale yield losses.
Benefits of Robotics in Precision Agriculture
✔ Increased Efficiency: Robots perform repetitive tasks faster and more accurately than humans, improving productivity.
✔ Resource Optimization: Precise application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides minimizes waste and environmental impact.
✔ Labor Shortage Solution: Automation reduces dependency on seasonal labor, addressing workforce shortages.
✔ Sustainability: Reduced chemical usage and optimized resource management promote eco-friendly farming.
✔ Higher Yields: Data-driven decision-making ensures optimal growing conditions, maximizing crop output.
Challenges and Future Prospects
- High Initial Investment: Advanced robotic systems require significant capital investment, limiting accessibility for small-scale farmers.
- Technical Complexity: Adoption requires training and integration with existing farm management systems.
- Connectivity Issues: Reliable internet and power infrastructure are necessary for seamless robotic operations, particularly in remote areas.
As advancements in AI, robotics, and IoT continue, precision agriculture will become more accessible and efficient. Future innovations will focus on autonomous farm networks, AI-driven decision-making, and enhanced sustainability practices, driving the next revolution in agriculture.
Stay ahead with ITBusinessNews – Your trusted source for Technology and Business news. Fast & Precise